PLOT | 目标区域的测序覆盖度作图
文章目录
不论是目标区域测序还是外显子组测序还是全基因组测序之后,我们会关注目标区域在特定深度下的覆盖度。比如20X的比例,50X的比例。如果只计算特定深度的覆盖度,我们了解不到其他深度下的覆盖度情况。如果每个都列出来,又不直观,这个时候用图片来表示就非常直观了。
获取统计数据
我们需要知道在每个深度下碱基的比例,这个时候强大的bedtools就出场了。
bedtools coverage -sorted -hist -g genome.file -b samp.bam -a target_regions.bed ' grep ^all > samp.hist.all.txt
-hist是为了获取目标区域的总结信息,以all开头,输出每个每个深度下碱基的比例,所以后续用grep ^all来过滤。
-sorted可以节省内存,但需要通过-g跟genome file来指定染色体的顺序。
genome file可以通过awk -v OFS='\t' {‘print $1,$2’} genome.fa.fai > genome.file 得到。
假设我们得到了smp1.hist.all.txt、smp2.hist.all.txt、smp3.hist.all.txt、smp4.hist.all.txt、smp5.hist.all.txt、smp6.hist.all.txt、smp7.hist.all.txt、
作图
|
|
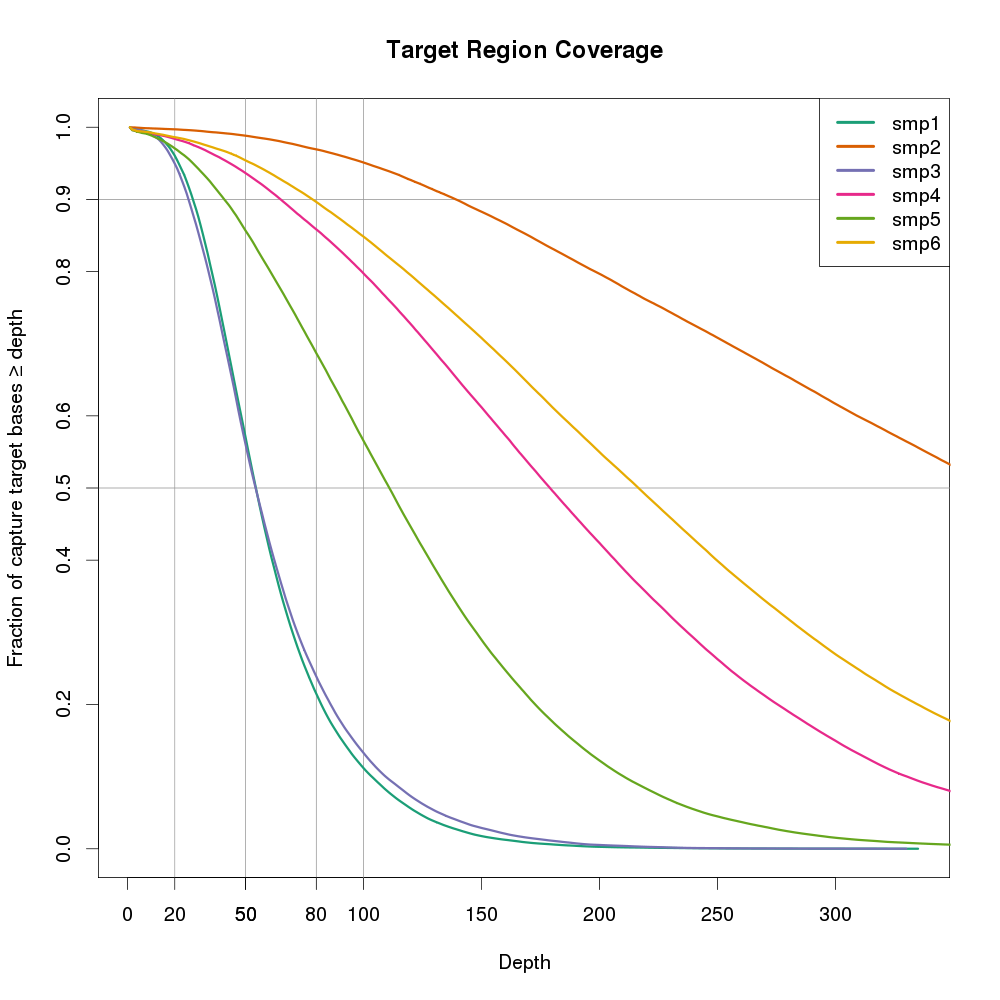
图片也可以用ggplot2来做。横坐标是DP,纵坐标是大于等于>=该DP的碱基比例。该图还有一个好处,是可以多个样本同时放在一张图上,便于进行样本间比较。
可以看出smp2的覆盖度最好,随着横左边的增加,下降最缓慢。smp1和smp3最不好,在20X以后,覆盖度显著下降。如果样本smp来自不同的测序实验,则smp2所用的方法是最有的。
最后还是那句话,图片表达的信息量多而且直观。让我们用图片说话。
主要CLONE参考:
http://www.gettinggeneticsdone.com/2014/03/visualize-coverage-exome-targeted-ngs-bedtools.html
####################################################################
#版权所有 转载请告知 版权归作者所有 如有侵权 一经发现 必将追究其法律责任
#Author: Jason
####################################################################
文章作者 zzx
上次更新 2018-02-01
